| [1] Jauregui JJ, Boylan MR, Kapadia BH, et al. Total joint arthroplasty in nonagenarians: what are the risks? J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(12): 2102-2105.[2] Springer BD, Beaver WB, Griffin WL, et al. Role of surgical dressings in total joint arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015;44(9):415-420.[3] Halawi MJ. Outcome measures in total joint arthroplasty: current status, challenges, and future directions. Orthopedics. 2015;38(8): e685-e689.[4] Daines BK, Dennis DA, Amann S. Infection prevention in total knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(6):356-364.[5] Aumiller WD, Kleuser TM. Recognizing and managing infections in total joint arthroplasty. JAAPA. 2015;28(6):37-41.[6] Gaspar MP, Kane PM, Shin EK. Management of complications of wrist arthroplasty and wrist fusion. Hand Clin. 2015;31(2):277-292.[7] Yu S, Garvin KL, Healy WL, et al. Preventing hospital readmissions and limiting the complications associated with total joint arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(11):e60-e71.[8] Takedani H, Ohnuma K, Hirose J. Deep venous thrombosis was not detected after total knee arthroplasty in Japanese patients with haemophilia. Haemophilia. 2015;21(5):585-588.[9] An TJ, Engstrom SM, Oelsner WK, et al. Elevated d-Dimer is not predictive of symptomatic deep venous thrombosis after total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(10):2269-2272.[10] Kim YH, Kulkarni SS, Park JW, et al. Prevalence of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism treated with mechanical compression device after total knee arthroplasty in Asian patients. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(9):1633-1637.[11] Westrich GH, Haas SB, Mosca P, et al. Meta-analysis of thromboembolic prophylaxis after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(6):795-800.[12] Imperiale TF, Speroff T. A meta-analysis of methods to prevent venous thromboembolism following total hip replacement. JAMA.1994;271 (22):1780-1785.[13] Gillespie W, Murray D, Gregg PJ, et al. Risks and benefits of prophylaxis against venous thromboembolism in orthopaedic surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(4):475-479.[14] Clarke MT, Green JS, Harper WM, et al. Screening for deep-venous thrombosis after hip and knee replacement without prophylaxis. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1997;79(5):787-791.[15] 邱贵兴. 中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2009,3(3):380-383.[16] Bell TH, Berta D, Ralley F, et al. Factors affecting perioperative blood loss and transfusion rates in primary total joint arthroplasty: a prospective analysis of 1642 patients. Can J Surg. 2009;52(4):295-301.[17] Raskob GE, Hirsh J. Controversies in timing of the first dose of anticoagulant prophylaxis against venous thromboembolism after major orthopedic surgery.. Chest. 2003;124(6):379S-385S.[18] 许杰,马若凡,李登,等. 肝硬化患者人工全髋关节置换围手术期深静脉血栓形成风险及个体化抗凝治疗的研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2015,35(11): 1096-1104.[19] 许杰,黄晶,马若凡,等.人工髋关节置换肝硬化患者围置换期的处理[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(52):8967-8973.[20] van Helmond N, Johnson BD, Curry TB, et al. Coagulation changes during lower body negative pressure and blood loss in humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;309(9):H1591-H1597.[21] Chapin JC, Hajjar KA. Fibrinolysis and the control of blood coagulation. Blood Rev. 2015;29(1):17-24.[22] Eckman MH, Erban JK, Singh SK, et al. Screening for the risk for bleeding or thrombosis. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138(3):W15-W24.[23] Mallett SV, Cox DJ. Thrombelastography. Br J Anaesth. 1992;69(3): 307-313.[24] Hartert H. Blutgerinnungsstudien mit der Thrombelastographie, einem neuen Untersuchungsverfahren. Klinische Wochenschrift. 1948;26(37): 577-583.[25] Pfanner G, Koscielny J, Pernerstorfer T, et al. Preoperative evaluation of the bleeding history. Recommendations of the working group on perioperative coagulation of the Austrian Society for Anaesthesia, Resuscitation and Intensive Care. Anaesthesist.2007;56(6): 604-611.[26] Spiess BD, Gillies BS, Chandler W, et al. Changes in transfusion therapy and reexploration rate after institution of a blood management program in cardiac surgical patients. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 1995;9(2):168-173.[27] Luddington RJ. Thrombelastography/thromboelastometry. Clin Lab Haematol. 2005;27(2):81-90.[28] Esnault P, Prunet B, Cungi PJ, et al. Thromboelastometric profile of unwashed shed blood after primary knee arthroplasty. Transfus Clin Biol. 2015;22(1):30-36.[29] Na HS, Shin HJ, Lee YJ, et al. The effect of tranexamic acid on blood coagulation in total hip replacement arthroplasty: rotational thromboelastographic(ROTEM(R)) analysis. Anaesthesia. 2016;71(1): 67-75.[30] Elliott A, Wetzel J, Roper T, et al. Thromboelastography in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke. 2015;10(2):194-201.[31] Kane I, Ong A, Orozco FR, et al. Thromboelastography predictive of death in trauma patients. Orthop Surg. 2015;7(1):26-30.[32] Tekkesin N, Tekkesin M, Kaso G. Thromboelastography for the monitoring of the antithrombotic effect of low-molecular-weight heparin after major orthopedic surgery. Anatol J Cardiol. 2015;15(11):932-937.[33] Ward CF, Meathe EA, Benumof JL, et al. A computer nomogram for blood loss replacement. Anesthesiology. 1980;53(3):S126.[34] Nadler SB, Hidalgo JH, Bloch T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962;51(2):224-232.[35] Hong E, Kang YS. Structural equation modeling on healthy menopausal transition. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2015;45(1):64-75.[36] Jacobucci R, Grimm KJ, McArdle JJ. Regularized structural equation modeling. Struct Equ Modeling. 2016;23(4):555-566.[37] Hasman A. An introduction to structural equation modeling. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2015;213:3-6.[38] Cook MR, Louis SG, McCully SP, et al. Positive blood alcohol is associated with reduced DVT in trauma. Injury. 2015;46(1):131-135.[39] Connelly CR, Yonge JD, McCully SP, et al. Assessment of three point-of-care platelet function assays in adult trauma patients. J Surg Res. 2017;212:260-269.[40] Connelly CR, Van PY, Hart KD, et al. Thrombelastography-based dosing of enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis in trauma and surgical patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Surg. 2016;151(10):e162069.[41] Konig G, Yazer MH, Waters JH. The effect of salvaged blood on coagulation function as measured by thromboelastography. Transfusion. 2013;53(6):1235-1239.[42] Kashuk JL, Moore EE, Wohlauer M, et al. Initial experiences with point-of-care rapid thrombelastography for management of life-threatening postinjury coagulopathy. Transfusion. 2011;52(1):23-33.[43] Klein SM, Slaughter TF, Vail PT, et al. Thromboelastography as a perioperative measure of anticoagulation resulting from low molecular weight heparin: a comparison with anti-Xa concentrations. Anesth Analg. 2000;91(5):1091-1095.[44] Yang Y, Yao Z, Dai W, et al. Changes of thrombelastography in patients undergoing elective primary total knee and total hip replacement with low molecular heparin prophylaxis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014;9:52.[45] Holcomb JB, Minei KM, Scerbo ML, et al. Admission rapid thrombelastography can replace conventional coagulation tests in the emergency department: experience with 1974 consecutive trauma patients. Ann Surg. 2012;256(3):476-486.[46] Wilson D, Cooke EA, McNally MA, et al. Changes in coagulability as measured by thrombelastography following surgery for proximal femoral fracture. Injury. 2001;32(10):765-770.[47] Vig S, Chitolie A, Bevan DH, et al. Thromboelastography: a reliable test? Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2001;12(7):555-561.[48] Dickinson KJ, Troxler M, Homer-Vanniasinkam S. The surgical application of point-of-care haemostasis and platelet function testing. Br J Surg. 2008;95(11):1317-1330.[49] Mccrath DJ, Cerboni E, Frumento RJ, et al. Thromboelastography maximum amplitude predicts postoperative thrombotic complications including myocardial infarction.. Anesthesia Analgesia. 2005;100(6): 1576-1583.[50] Bai J, Zheng QW, Fu SH, et al. Association between thrombelastography system and thromboembolic and bleeding events in Chinese aged people. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2013;6(4):310-319. |
.jpg)
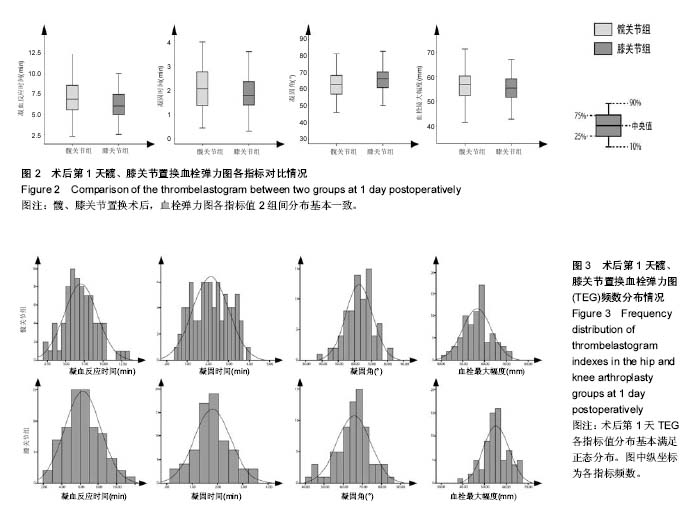
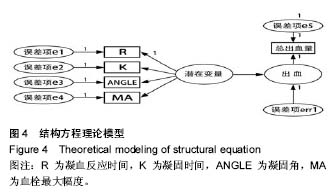
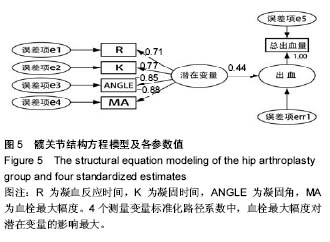
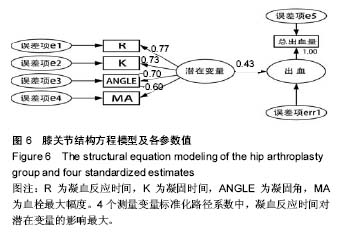
.jpg)